General Chemistry Questions on Acids/Bases/Salts – Calculations (includes Balancing Redox
- 1.How many grams of Ca(OH)2 are contained in 1500 mL of 0.0250 M Ca(OH)2 solution?
- (a) 3.17 g
- (b) 2.78 g
- (c) 1.85 g
- (d) 2.34 g
- (e) 4.25 g
- 2.What volume of 12.6 M HCl must be added to enough water to prepare 5.00 liters of 3.00 M HCl?
- (a) 1.19 L
- (b) 21.0 L
- (c) 0.840 L
- (d) 7.56 L
- (e) 2.14 L
- 3.What is the molarity of the salt produced in the reaction of 200 mL of 0.100 M HCl with 100 mL of 0.500 M KOH?
- (a) 0.0325 M
- (b) 0.0472 M
- (c) 0.0667 M
- (d) 0.0864 M
- (e) 0.0935 M
- 4.What volume of 0.50 M KOH would be required to neutralize completely 500 mL of 0.25 M H3PO4 solution?
- (a) 2.5 x 102 mL
- (b) 1.4 x 103 mL
- (c) 83 mL
- (d) 7.5 x 102 mL
- (e) 5.2 x 102 mL
- 5.A 0.6745 gram sample of KHP reacts with 41.75 mL of KOH solution for complete neutralization. What is the molarity of the KOH solution? (Molecular weight of KHP = 204 g/mol. KHP has one acidic hydrogen.)
- (a) 0.158 M
- (b) 0.099 M
- (c) 0.139 M
- (d) 0.079 M
- (e) 0.061 M
- 6.How many equivalents of phosphoric acid are contained in 300 mL of 4.00 M phosphoric acid? (Assume the acid is to be completely neutralized by a base.)
- (a) 0.600 eq
- (b) 1.20 eq
- (c) 2.40 eq
- (d) 3.60 eq
- (e) 4.80 eq
- 7.Calculate the normality of a solution that contains 4.5 g of (COOH)2 in 3000 mL of solution? (Assume the (COOH)2 is to be completely neutralized in an acid-base reaction.)
- (a) 0.033 N
- (b) 0.045 N
- (c) 0.066 N
- (d) 0.090 N
- (e) 0.12 N
- 8.What volume of 0.100 N HNO3 is required to neutralize 50.0 mL of a 0.150 N solution of Ba(OH)2?
- (a) 50.0 mL
- (b) 75.0 mL
- (c) 100. mL
- (d) 125 mL
- (e) 150. mL
- 9.How many grams of NaOH would be required to neutralize all the acid in 75.0 mL of 0.0900 N H2SO4?
- (a) 0.540 g
- (b) 0.270 g
- (c) 1.32 g
- (d) 0.660 g
- (e) 0.859 g
- 10.What is the oxidation number for carbon in CaC2O4?
- (a) 0
- (b) +2
- (c) +3
- (d) +4
- (e) +6
- 11.Balance the molecular equation for the following redox reaction. What is the sum of the coefficients? Don’t forget coefficients of one. Use the smallest whole number coefficients possible.
H2SO4(aq) + HI(aq)  I2(s) + SO2(g)
I2(s) + SO2(g)- (a) 7
- (b) 9
- (c) 11
- (d) 13
- (e) 5
- 12.For the reaction between permanganate ion and sufite ion in basic solution, the unbalanced equation is:
MnO4– + SO32-  MnO2 + SO42-
MnO2 + SO42-
When this equation is balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients possible, the number of OH– ions is- (a) two on the right.
- (b) two on the left.
- (c) three on the right.
- (d) four on the right.
- (e) four on the left.
- 13.Balance the following redox equation in acidic solution with the smallest whole number coefficients possible. What is the sum of all the coefficients? (Do not forget coefficients of one.)
Cu + SO42-  Cu2+ + SO2 (in acidic solution)
Cu2+ + SO2 (in acidic solution)- (a) 9
- (b) 10
- (c) 11
- (d) 12
- (e) 13
- 14.When the following equation is balanced with the smallest possible set of integers, what is the sum of all the coefficients? (Do not forget coefficients of one.)
Cr2O72- + H2S 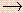 Cr3+ + S (in acidic solution)
Cr3+ + S (in acidic solution)- (a) 13
- (b) 24
- (c) 19
- (d) 7
- (e) 29
- 15.When the following equation is balanced with the smallest possible set of integers, what is the sum of all the coefficients? (Do not forget coefficients of one.)
MnO4– + Se2- 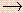 MnO2 + Se (in basic solution)
MnO2 + Se (in basic solution)- (a) 20
- (b) 22
- (c) 24
- (d) 26
- (e) 28
- 16.Consider the following unbalanced equation in acidic solution:
NaClO3 + H2O + I2 A 25.0 mL sample of 0.0833 M NaClO3 reacted with 30.0 mL of an aqueous solution of I2. How many grams of I2 were contained in the I2 solution?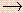 HIO3 + NaCl
HIO3 + NaCl- (a) 0.264 g
- (b) 0.397 g
- (c) 0.236 g
- (d) 0.159 g
- (e) 0.317 g
- 17.Consider the following unbalanced net ionic equation:
NO2– + MnO4– What is the molarity of a sodium nitrite, NaNO2, solution if 30.0 mL of it just reacts with 0.238 grams of KMnO4?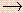 NO3– + Mn2+ (in acidic solution)
NO3– + Mn2+ (in acidic solution)- (a) 0.410 M
- (b) 0.126 M
- (c) 0.0502 M
- (d) 0.251 M
- (e) 0.0316 M
- 18.What is the equivalent weight (in grams) of copper(II) nitrate for use in a reaction involving the conversion of copper(II) to copper metal?
- (a) 46.9 g/eq
- (b) 93.8 g/eq
- (c) 187.6 g/eq
- (d) 375.2 g/eq
- (e) 562.8 g/eq
- 19.What is the normality of a K2Cr2O7 solution prepared by dissolving 5.00 g of K2Cr2O7 in 200 mL of solution, which will be used in the following unbalanced reaction?
Cr2O72– + SO32– 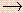 Cr3+ + SO42– (in acidic solution)
Cr3+ + SO42– (in acidic solution)- (a) 0.733 N
- (b) 0.226 N
- (c) 0.510 N
- (d) 0.441 N
- (e) 0.810 N
- 20.What mass of KMnO4 must be dissolved to prepare 1.25 L of 0.110 N KMnO4 solution? It is used in the reaction in which MnO4– ions oxidize Fe2+ into Fe3+ ions and are reduced to Mn2+ ions under acidic conditions?
- (a) 4.34 g
- (b) 23.8 g
- (c) 115 g
- (d) 19.1 g
- (e) 70.6 g
- 21.A 0.250 M solution of Na2C2O4 is to be used in a reaction in which the C2O42– will be oxidized to CO2. What is the normality of this Na2C2O4 solution?
- (a) 0.250 N
- (b) 1.00 N
- (c) 0.125 N
- (d) 0.0625 N
- (e) 0.500 N
- 22.What volume of a 0.150 N KI solution is required to react in basic solution with 34.1 mL of a 0.216 N solution of KMnO4? The products in the reaction include MnO2 and IO3–.
- (a) 25.4 mL
- (b) 37.9 mL
- (c) 12.6 mL
- (d) 98.2 mL
- (e) 49.1 mL
- 23.Calculate the normality of a NaClO solution if 35.00 mL of the solution is required to react with 0.615 g of Zn according to the following unbalanced equation:
Zn + ClO– 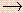 Zn(OH)2 + Cl– (in basic solution)
Zn(OH)2 + Cl– (in basic solution)- (a) 0.537 N
- (b) 0.275 N
- (c) 0.108 N
- (d) 0.366 N
- (e) 0.791 N
- 24.A solution of nitrous acid was standardized in a reaction where HNO2
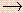 NO3– and its concentration was determined to be 0.100 N nitrous acid. What volume of this 0.100 N nitrous acid solution would be required to oxidation of 0.200 g of CoCl2 to CoCl3 according to the following net ionic equation?
NO3– and its concentration was determined to be 0.100 N nitrous acid. What volume of this 0.100 N nitrous acid solution would be required to oxidation of 0.200 g of CoCl2 to CoCl3 according to the following net ionic equation? Co2+ + HNO2 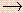 Co3+ + NO (in acidic solution)
Co3+ + NO (in acidic solution)- (a) 33.9 mL
- (b) 15.4 mL
- (c) 7.70 mL
- (d) 67.8 mL
- (e) 30.8 mL
- 25.What is the sum of all coefficients when the following net ionic equation is balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients possible? Do not forget coefficients of one.
MnO4– + Mn2+ 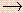 MnO2 (in basic solution)
MnO2 (in basic solution)- (a) 19
- (b) 16
- (c) 13
- (d) 11
- (e) 7
Answers:
1. (b) 2. (a) 3. (c) 4. (d) 5. (d) 6. (d) 7. (a) 8. (b) 9. (b) 10. (c) 11. (a) 12. (a) 13. (b) 14. (b) 15. (b) 16. (e) 17. (b) 18. (b) 19. (c) 20. (a) 21. (e) 22. (e) 23. (a) 24. (e) 25. (b)